Technical SEO issues can go unnoticed for a long time, causing a significant effect on a site’s visibility.
For example, a simple change in your Robots.txt can block search bots from crawling your website and tank your site’s ratings.
Wondering why more content and backlinks are not improving your rankings? You may need to spot and resolve technical SEO issues. And monitor from time to time.
In this guide, I’ll highlight the common technical SEO issues your website may have and how you can resolve them effectively.
Let’s get started.
| Summary 10 Common Technical SEO Issues Crawling and Indexability Issues Pages Restricted with Robots.txt Wrongly placed “Noindex” Tags Duplicate content Broken links HTTP status code issues On-Page SEO Issues Title Tags and Meta Descriptions Image optimization issues Improper use of header tags Structured data Thin content |
Crawling and Indexability Issues
Crawling is the process used by search engine bots to discover and analyze web pages. Indexing involves organizing and storing the crawled pages in search engine databases.
Crawling and indexing issues prevent search engines from accessing your website and affect your website’s visibility on search results.
Here are the common crawling and indexing issues that affect Technical SEO and how to fix them.
1. Pages Restricted with Robots.txt
A robots.txt file—placed in the root directory on your website instructs Search crawlers which pages they should crawl on your site.
Search engine bots first check your site’s robots.txt file to check which pages are off-limits.
A misconfigured robots.txt file can prevent important pages or your entire website from being crawled, preventing your website from appearing on search results.
Solution
To check the robots.txt instructions on your website, type www.yoursite.com/robots.txt
Here’s how a blocked robots.txt file will appear, meaning your website cannot be crawled.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
To fix the issue, adjust your robots.txt file to grant access to search engine bots to crawl the necessary pages. Simply replace the “disallow” with “allow” to appear as follows:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
If you still need to block some pages, use Google Search Console’s robots.txt tester tool to confirm the pages you need to be blocked from crawlers.
2. Wrongly placed “Noindex” Tags
“Noindex” tags are directives that instruct search engines not to index a specific web page and control crawling.
They prevent certain pages from appearing on Search results.
A noindex tag appears like:
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
Solution
You can remove a “noindex” directive from the pages you want indexed.
Run a crawl of your website with Semrush’s Site Audit. On the “issues” tab, the tool will list the pages with a “noindex” tag. Some of the pages with noindex issues may correctly be labeled for your SEO control—if you don’t want valuable content to be discovered.
Once you identify pages that shouldn’t be on your “noindex Issues report” on your Site Audit tool, simply remove the tag and verify that they aren’t blocked by robot.txt.
3. Duplicate content
Just like the name, duplicate content involves writing about the same thing on different pages of your website.
Duplicate content results in identical or substantially similar content appearing in multiple places on the same website.
Duplicate content makes it difficult for search engines to determine which version of the content should be ranked for relevant search queries. It also leads to crawl budget wastage and may also cause a poor user experience.
How to resolve duplicate content issues
To identify duplicate content issues on your website, use the Semrush Site Audit tool to run a crawl. The tool flags 85% of similarities in content as duplicate.

Here’s how to resolve duplicate content issues that may be harming your technical issues:
- Implement canonical tags to specify your preferred version of the multiple pages with similar content.
- Set up 301 redirects to redirect multiple pages to the page you want search bots to rank.
- Use robots.txt to prevent crawls on the pages with low-value content.
- Consolidate similar articles to create a single authoritative non-duplicated page.
4. Broken links
Broken links are URLs that lead nowhere or to unavailable web pages.
When a crawler encounters a broken link, it typically stops following it. Broken links disrupt the crawling and indexing process and make it impossible for pages to be crawled and discovered.
Broken links also frustrate your users and may increase your bounce rate. Your website can easily be perceived as unreliable and of poor quality.
Fixing broken links
On your Semrush site audit tool, look for broken internal links under “issues”. Update or remove the links altogether.

After fixing your broken pages, check if your site has orphan pages— pages without internal links.
Web crawlers can only access orphan pages from a sitemap or backlinks, limiting their discoverability. Orphan pages are not connected to your internal site structure, meaning no linking equity flows to them.
On your “Issues” tab, search for orphan pages. After identifying them, fix them by linking with relevant internal pages.
5. HTTP status code issues
Different HTTP status code issues can impact crawling, indexing, and user experience.
Here are different HTTP status codes, the cause, and the impact:
| HTTP status code | Interpretation | SEO impact |
| 404 Not Found | The requested page is not found by the search engine. | Poor user experience Higher bounce rateBroken links |
| 302 Redirects | Temporary redirect | If not changed to a 301 (permanent redirect), value may not be moved and assigned to the right page. |
| Soft 404 | Page returns a “200 OK” but actually contains a “404 Not Found” | Pages may be indexed and cause a poor user experience. |
| Blocked 4xx | Client-side errors (e.g., 400 Bad Request, 403 Forbidden) | Search crawlers may struggle to crawl and index the pages. May portray the website as insecure. |
You can use your Google Search Console to see the different status codes of different URLs.
Go to “URL inspection,” enter a URL then “View Crawled Page,” then “Status”.
To check specific error codes, use the Semrush Site Audit tool. On the “Issues” tab, you’ll see the number of crawled pages with different status codes.
Here’s how to fix the different status code issues:
- Implement a 301 redirect to the pages with 404 Not Found errors.
- Change 302 redirects to 301 redirects
- Identify specific issues on your website causing blocked 4xx codes and address them accordingly.
- Resolve Soft 404 Errors and ensure that your server returns the correct status code (usually 404) for pages that don’t exist.
On-Page SEO Issues
Your web pages should be attractive to search engines and provide an excellent user experience.
On-page SEO issues affect your site’s visibility and may reduce the flow of organic traffic.
Let’s look at on-page technical SEO issues.
6. Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
A title tag defines your page to search bots, helping them establish the page’s relevance to a user’s search query.
A meta description gives a brief summary of your page’s content to the user on the search query, giving a first impression to a user.
Well-optimized title tags and meta descriptions provide context, relevance, and a compelling reason for users to click on your website.
To check if these are well optimized, simply head to the Semrush Site Audit tool on the project created earlier. Click on the ON-Page SEO checker and identify any highlighted issues.
Some issues may include duplicate or missing meta descriptions and titles.
Solution
Here are some guidelines for resolving title tags and Meta-description issues:
- Create a unique title and meta description tag for each page to avoid duplication.
- Use the title to describe each page accurately.
- Keep the title tag under a length of 60 characters and the meta description under 155 characters.
- Use the main keyword in the title and 2 or 3 head keywords in the meta description.
- Add your competitive advantage to the title, e.g., price discount offers.
- Keep your title tags and meta descriptions optimized for mobile users to avoid losing that significant mobile traffic which accounts for over 60% of Google Searches.
7. Image optimization issues
Image optimization in SEO involves preparing and formatting images to improve user experience and search engine visibility.
It involves delivering images in the right format, size and resolution for a better user experience and adding the right metadata in the labelling to give content to search crawlers.
Image searches make up to 22% of all Google searches.
Image optimization issues can lead to slow page loading times, creating a negative user experience, reducing your site’s accessibility, and lowering your SEO rankings.
Here are a few image optimization issues:
- Large file sizes that take long to load, slowing loading times.
- Images that cannot compress without affecting their quality
- Images in the wrong formats, other than JPEG and PNG
- Unresponsive to different screen sizes
- Images without alt texts
Solution
To check for image optimization issues, head over to the Issues tab on your Site Audit tool. The Issue report will highlight any Errors, Warnings and Notices.
Look under the “Warnings” for broken images.
Under the “Notices’, you’ll find the images on your site with optimization issues.
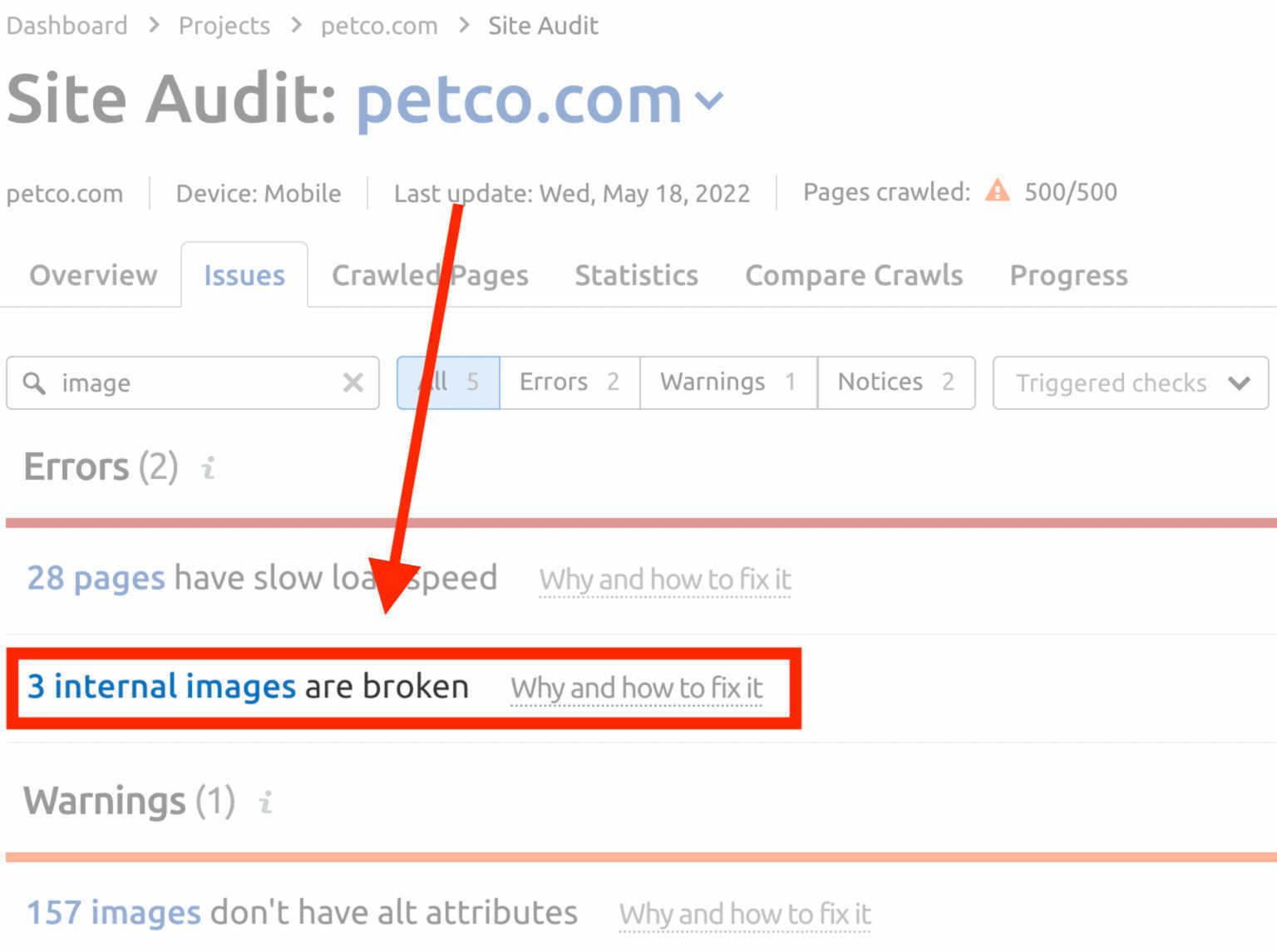
To resolve image optimization issues:
- Fix the broken images and add alt attributes to the highlighted images through your CMS.
- Use image compression tools like TinyImage and Adobe Photoshop to compress the images for faster load times.
- Implement responsive image designs for different screen sizes.
8. Improper use of header tags
Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are HTML that show the structure of your web content and define the hierarchy of the headings and subheadings.
Header tags organize content and make it more readable for users and machines. They provide a semantic structure to your content and can be used for keyword optimization.
H1 tag is used for the page title, while H2-H6 tags show the sub-sections, creating a hierarchical structure.
To check for header tag issues, check your Semrush Site Audit tool’s “Issues” tab. Type H1 to check for warnings on pages without H1 tags.

Fixing header tag issues
Here’s how to optimize your header tags for on-page SEO:
- Use one H1 per page
- Add keywords in the headers and place them naturally
- Ensure your H1 tags are similar to your title tags
- Keep each heading descriptive and relevant to the content it introduces
9. Structured data
Also known as schema markup, structured data is an HTML code added to a website to give specific information about a page’s content to search engines.
Schema helps search engines understand and display your page’s content on search results.
For example., a recipe schema markup will show cooking time, ingredients, star ratings, etc.—information that search engines can pick and generate a rich snippet on SERPs for users.
Here are different ways structured data can improve your on-page SEO:
- Improved visibility since rich snippets stand out for being eye-catching and informative.
- Featured snippets increase the likelihood of your content appearing on top of search results.
- Structured data make it easier for your content to appear in voice search by giving precise answers to voice search queries.
Fixing structured data issues
You can identify which URLs on your website are eligible for rich results using the Site Audit tool.
For example, if a competing site that outranks you has a SERP feature, find out which markup you can implement on your page. Google defines 29 Structured data items and you can find out which items are ideal for your website.
10. Thin content
Thin content refers to web pages that offer little or no value to users. The content lacks depth, quality and relevance, making it just not useful, and causing a poor user experience.
Google’s Helpful Content Update shows that the Search engine prioritizes content that gives a satisfying experience to users, rewarding sites that offer high-quality content.
Thin content can include short blog posts, pages with inadequate text, irrelevant affiliate pages, etc.
Since it lacks substance and relevance, thin content is bad for SEO. It can increase bounce rates, lower engagement, and reduce organic traffic.
Solution
To identify thin content on your website, look at “Site Health” on your Semrush Site Audit dashboard.
The Site Health score highlights errors, warnings and notices on your website. Click on the “Issues” tab to identify URLs that may have thin content.
Read further on our detailed guide on how to create an effective content strategy and avoid thin content.
You can also analyze your web pages and look for pages with short non-informative content, duplicate content, user feedback, or pages without keyword relevance.
Let’s look at quick tips you can use to fix thin content:
- Use keywords to create relevant content and optimize the page.
- Add valuable information that addresses user needs and queries
- Expand existing content to provide more depth, examples, and explanations
- Improve readability with better headings, bullet points, and images
- Remove redundant pages and consolidate their content in better-performing pages.
One More Thing!
Remember to check your site regularly for page speed issues and mobile-friendliness. A fast-loading mobile-friendly provides an excellent user experience and helps your website to remain competitive on SERPs.
Optimizing your website for peak SEO performance should be a regular exercise. Especially if you regularly add new content, backlinks, and details.
Check out our comprehensive SEO checklist and keep your site in perfect SEO health.
Do you need a review of your site’s health, contact me now and get your site well-optimized for Google and other search engines. We also offer well-written yet affordable SEO content.
Did I miss something? Let’s discuss on LinkedIn or on the comment section below.